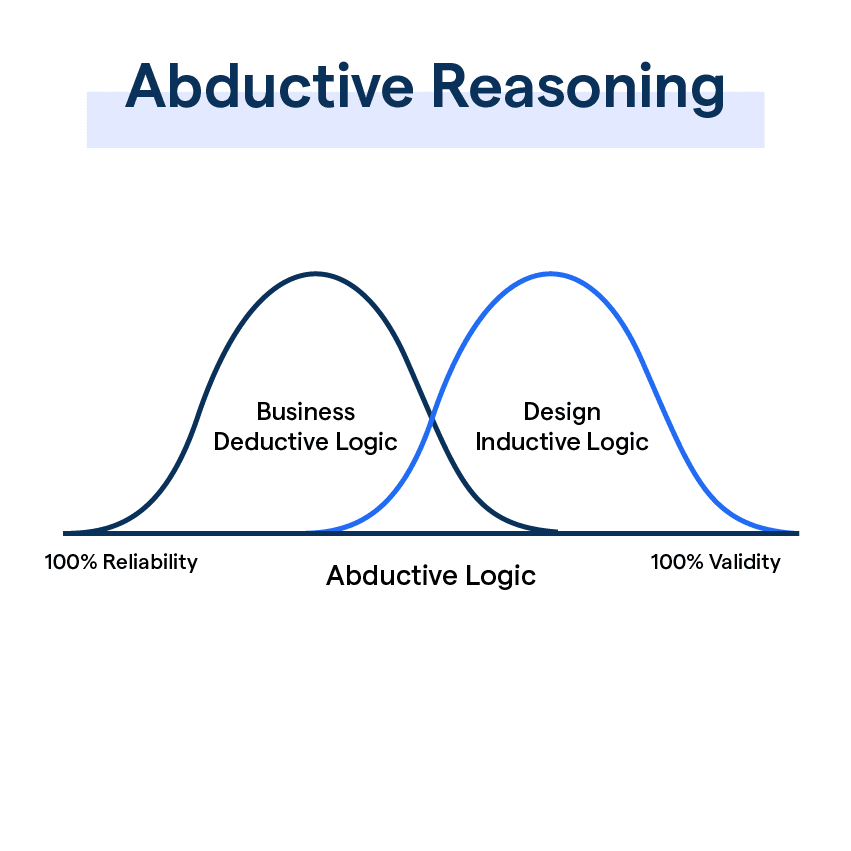
Abductive reasoning is a form of logical inference that involves making educated guesses or hypotheses to explain observations or phenomena. Unlike deductive reasoning, which involves drawing specific conclusions based on established premises, abductive reasoning is more exploratory and speculative in nature.
In the context of artificial intelligence (AI), abductive reasoning plays a crucial role in the process of problem-solving and decision-making. AI systems use abductive reasoning to generate possible explanations for a given set of data or observations, which can then be further analyzed and tested to determine their validity.
One of the key advantages of abductive reasoning in AI is its ability to handle uncertainty and incomplete information. In real-world scenarios, data is often noisy or ambiguous, making it difficult to arrive at definitive conclusions using traditional deductive methods. Abductive reasoning allows AI systems to make informed guesses and fill in the gaps in knowledge, leading to more robust and flexible decision-making processes.
In addition to its practical applications in AI, abductive reasoning also has theoretical implications for understanding human cognition. Cognitive scientists have long studied how humans use abductive reasoning to make sense of the world around them and form hypotheses about the underlying causes of events. By incorporating these insights into AI systems, researchers hope to develop more human-like and intelligent machines that can adapt to new situations and learn from experience.
Overall, abductive reasoning is a powerful tool in the AI toolkit that enables machines to think critically, reason effectively, and solve complex problems in a way that mirrors human thought processes. By harnessing the power of abductive reasoning, AI systems can enhance their decision-making capabilities and improve their overall performance in a wide range of applications, from healthcare and finance to autonomous driving and natural language processing.
1. Abductive reasoning is a crucial aspect of artificial intelligence as it allows machines to make educated guesses and draw conclusions based on incomplete information, similar to how humans make decisions.
2. By incorporating abductive reasoning into AI systems, machines can better understand and interpret ambiguous or uncertain data, leading to more accurate and reliable outcomes.
3. This form of reasoning is essential in problem-solving tasks where there is a need to infer the most likely explanation or hypothesis from a set of observations, making it a valuable tool in various AI applications.
4. Implementing abductive reasoning in AI algorithms can enhance the overall decision-making process, enabling machines to adapt and learn from new information and improve their problem-solving capabilities over time.
5. Overall, the significance of abductive reasoning in AI lies in its ability to bridge the gap between data and conclusions, allowing machines to think more critically and make informed decisions in complex and uncertain situations.
1. Medical Diagnosis: Abductive reasoning is used in AI systems to help doctors and healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses by analyzing symptoms and potential causes.
2. Fraud Detection: AI algorithms use abductive reasoning to detect patterns and anomalies in financial transactions, helping to identify potential cases of fraud.
3. Natural Language Processing: Abductive reasoning is applied in NLP systems to interpret and understand the meaning of ambiguous or incomplete language inputs.
4. Autonomous Vehicles: AI-powered autonomous vehicles use abductive reasoning to make decisions and navigate complex environments by analyzing sensor data and predicting potential outcomes.
5. Predictive Maintenance: Abductive reasoning is used in AI systems to predict equipment failures and maintenance needs by analyzing historical data and identifying potential causes of malfunctions.
There are no results matching your search.
ResetThere are no results matching your search.
Reset